Networking Terminals for SamTouch
SamTouch can communicate with other terminals that have SamTouch installed on it as well. Here we will run through how to network SamTouch terminals and troubleshoot issues you may come across when doing so.
The first thing that we will need to do is make sure that the terminals are connected to each other via some form of network. Where possible, using hard-wired ethernet over WiFi is recommended as this is much more reliable. Internet is not required for the terminals to link and talk to each other however internet will be required should the customer want to use the SamTouch Office Cloud solution, or any other internet required integrations. Furthermore, crossover cables can be used but this is only when you are linking one terminal directly to one other terminal, if you are wanting to link more then you will need a hub and straight-through Ethernet cables.
Setting a Manual IP Address
As default your IP address will be obtained automatically by Windows. In some instances, this may work without having to configure the IP address, however in other situations you may need to define this manually through Windows. It is recommended that manual IP addresses are set as this will prevent conflict of IPs later down the line. If you are using a hub without a router then you can set this up with a generic IP address (i.e. Terminal has an IP of 192.168.1.11, Subnet mask of 255.255.255.0 and a gateway of 192.168.1.1) however if you are using a hub with a router then you will need to determine what gateway the router is using Command Prompt. To do this, you will need to do the following:
- On the Windows Search bar, type the following:
- This should show an option for Command Prompt. Click on this, which should open a new window.
- In this window, enter the following line: ipconfig
- You will now be presented with a few lines of data, the key things we are looking for are:
- IPv4 Address
- Subnet Mask
- Default Gateway
- Make a note of these as we will need them shortly

Now that we have obtained what IP address the router has given us, we can proceed to setting this to a Static IP address. In order to do so, you will need to do the following:
- From the desktop, on the bottom right of the screen, right click the network icon (this will look a little PC window with an ethernet cable to the right of it, or it will look like a WiFi symbol) and click Open Network and Sharing Centre
- This will open the Network and Sharing Centre, on the right-hand side click the option which says Change adapter settings
- This will now show your network connections, right click the one you are using and click Properties
- Another window will now show, click the option which says Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) and click Properties
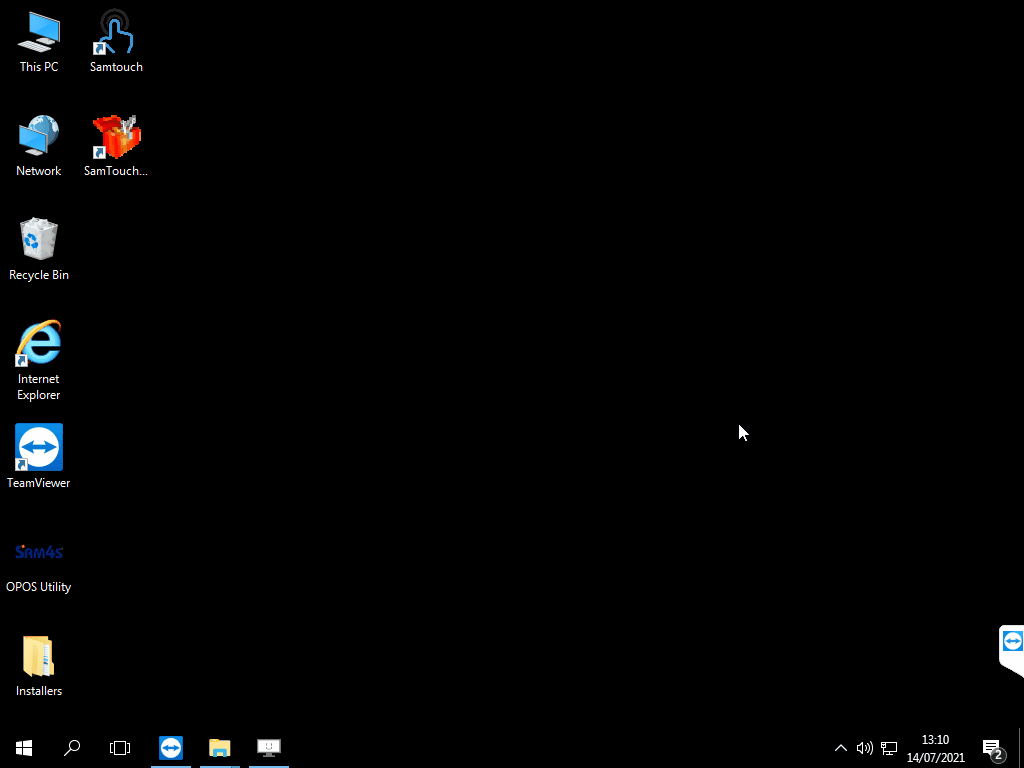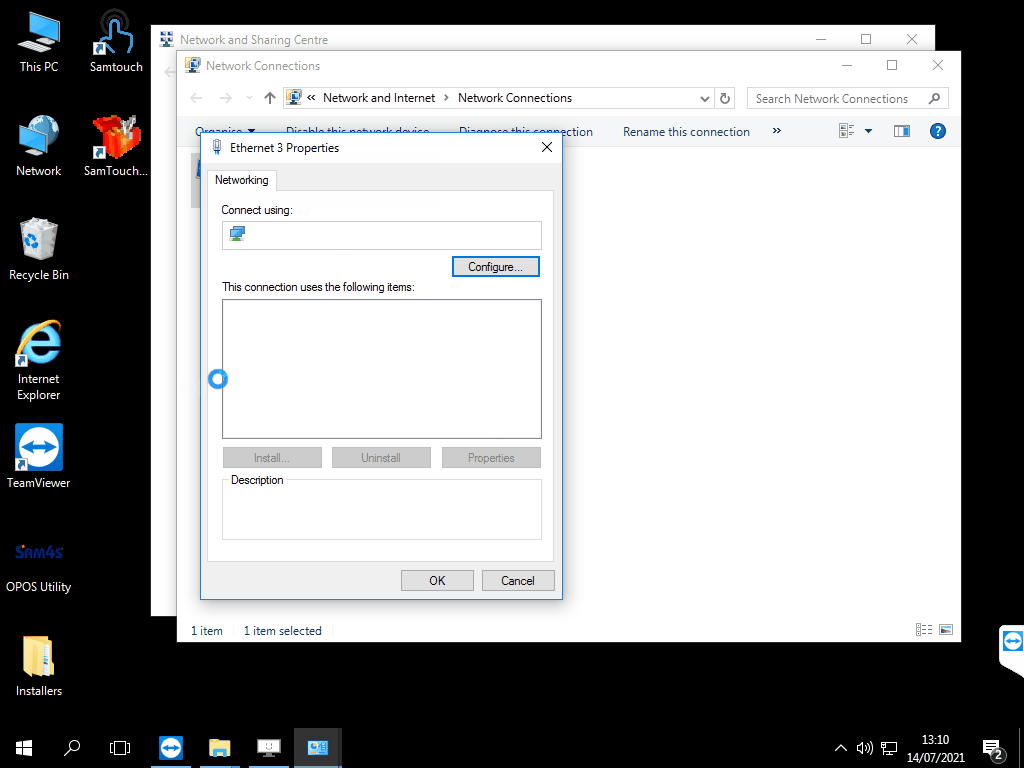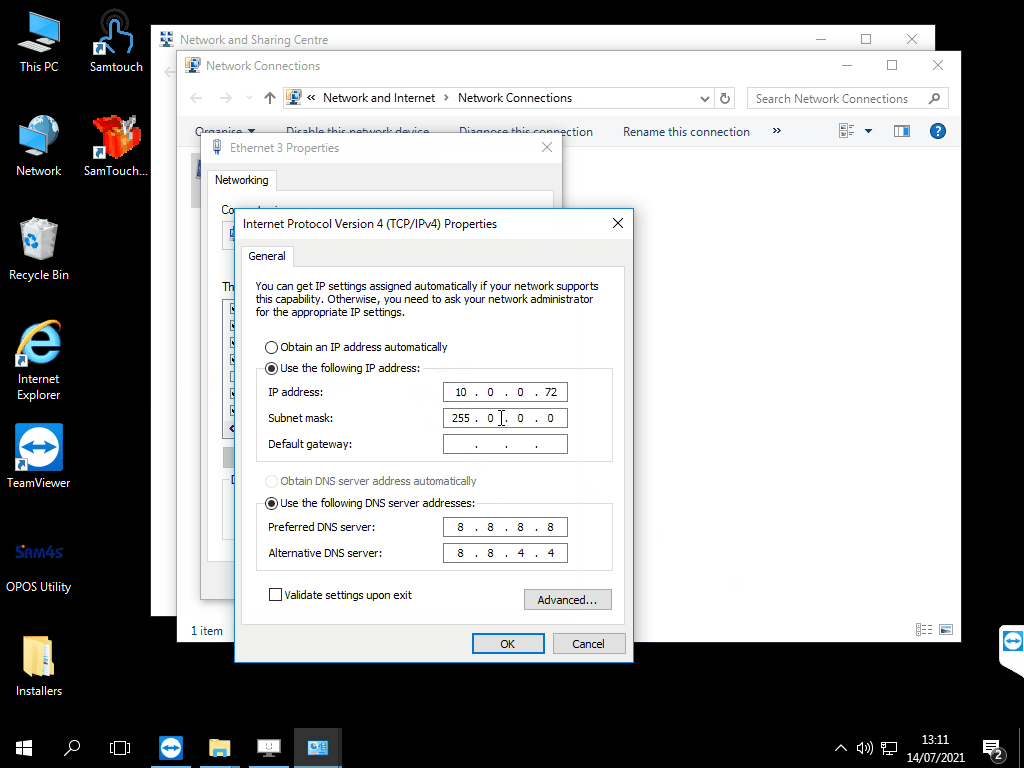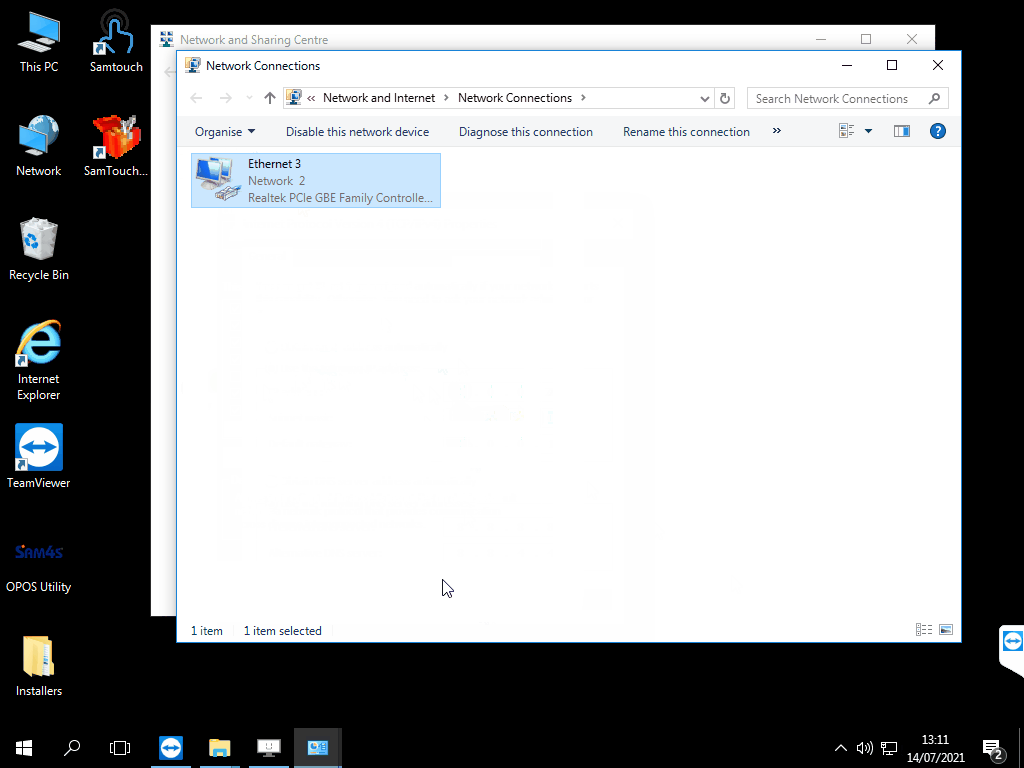
- Again, another window will open. You will want to choose the radio button which says Use the following IP address:
- If you are using a router for internet, you will now want to take the information we took earlier from Command Prompt and enter it into the relevant fields here. If you are not using a router we can enter a standard IP range, so for example:
- IP Address: 192.168.1.11 (This would be for terminal 1, if you had another terminal, you would set this to 192.168.1.12, terminal 3 = 192.168.1.13 etc.)
- Subnet mask: 255.255.255.0
- Default gateway: 192.168.1.1
- Once you have entered in the IP settings, click Okay, Close and then close all other windows.
You should now have set a static IP for your terminal.
Using the SamTouch Configuration Tool
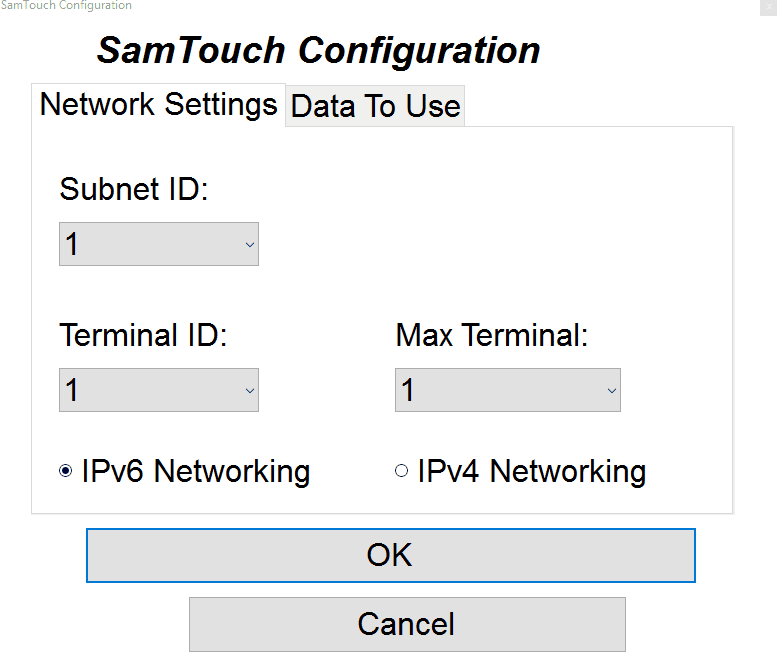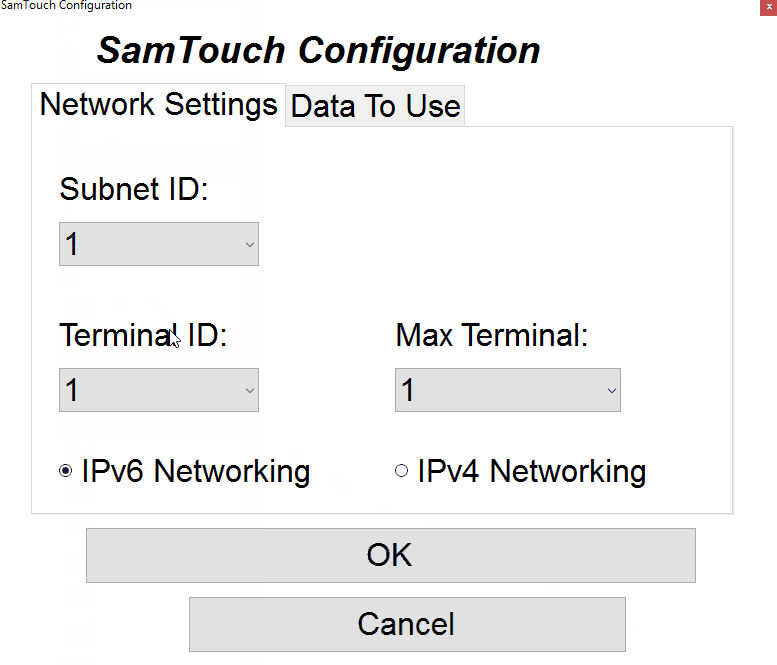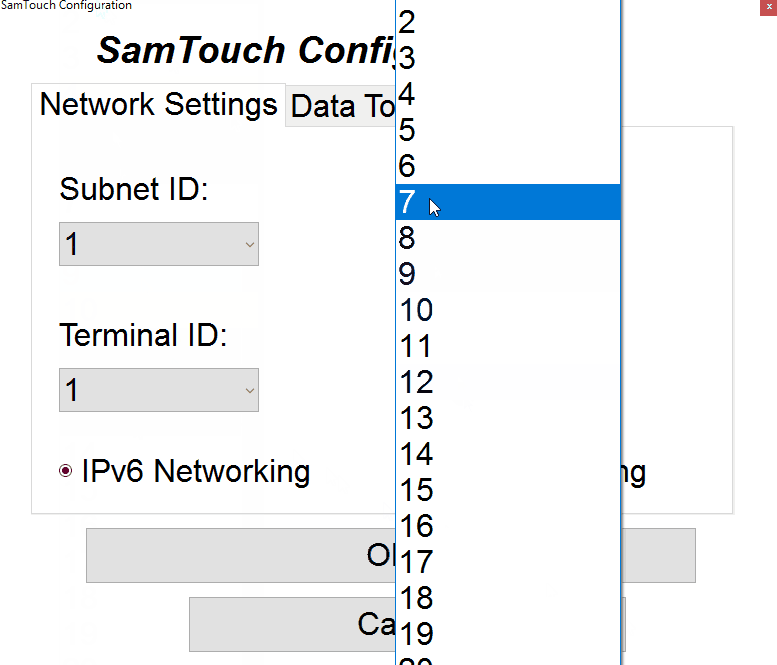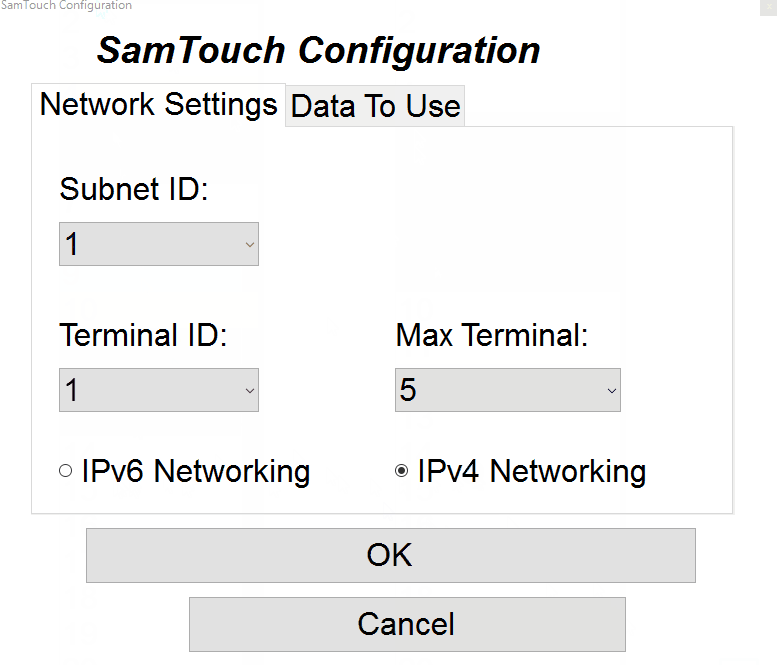
Now that we have a setup our IPs, we can now tell SamTouch how many terminals are in the network and set the terminal numbers. This can be done using the SamTouch Configuration tool which you should be able to see on the desktop, the icon being a little red toolbox (can also be found in the C: drive -> Samtouch folder). If you double click this it will open the configuration window. You will now be able to set the following options:
- Subnet ID: The subnet ID is used to tell SamTouch which range they are in, so if you have 4 terminals and you would want them all to be linked together, you will want them all to be in the same subnet ID. However, if you have 4 terminals and you want to 2 of them linked together, and the other 2 linked together separately, you would put the first set of terminals into Subnet ID 1 and then the second set of terminals into Subnet ID 2. By doing this, these 2 pairs of terminals will only communicate with the other till within its Subnet ID and will not conflict with the other pair of terminals.
- Terminal ID: This is the number of the terminal you are on, so your first terminal would want to be set to Terminal ID 1, your second to Terminal ID 2, third to ID 3 etc.
- Max Terminal: This is the max number of terminals in the system, so only set this to the number of terminals you have.
Please note: if for any reason you should ever need to remove the main terminal from the system which is the master for checks, clerks etc, do not set another terminal to be terminal 1 whilst it is out of the system as changing terminal IDs after the system has been in use can have negative effects, instead, you will need to go to your Network Settings within SamTouch and change which terminal is the master in there.
You should now have a linked SamTouch system. You can make sure this is the case by launching SamTouch on each terminal and if the bottom left chain icon is linked on every machine, then they are all talking to each other.
Troubleshooting
There may be some occasions where even after defining IPs and using the SamTouch configuration tool the terminals will still not communicate. If this is the case, there are a few troubleshooting methods we can attempt to resolve this.
Can the terminals see each other outside of SamTouch?
The first thing to check before anything else is whether the terminals can each see each other over the network. The way we can check this is by running a ping command within Command Prompt. To do this: –
- Go to the Windows search bar at the bottom left
- Enter cmd into the search bar and select Command Prompt that displays above
- On the new window, enter into the command line the following: ping ip address one of the other terminals. So, for example: ping 192.168.1.12. You can also type ipconfig to find out the IP information of the machine you are on
This will now attempt to ping the other terminal. You will get one of 2 outcomes. If you get something along the lines of: Reply from 192.168.1.12: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=255 and this repeats 3 more times then the terminals can see each other over the network.
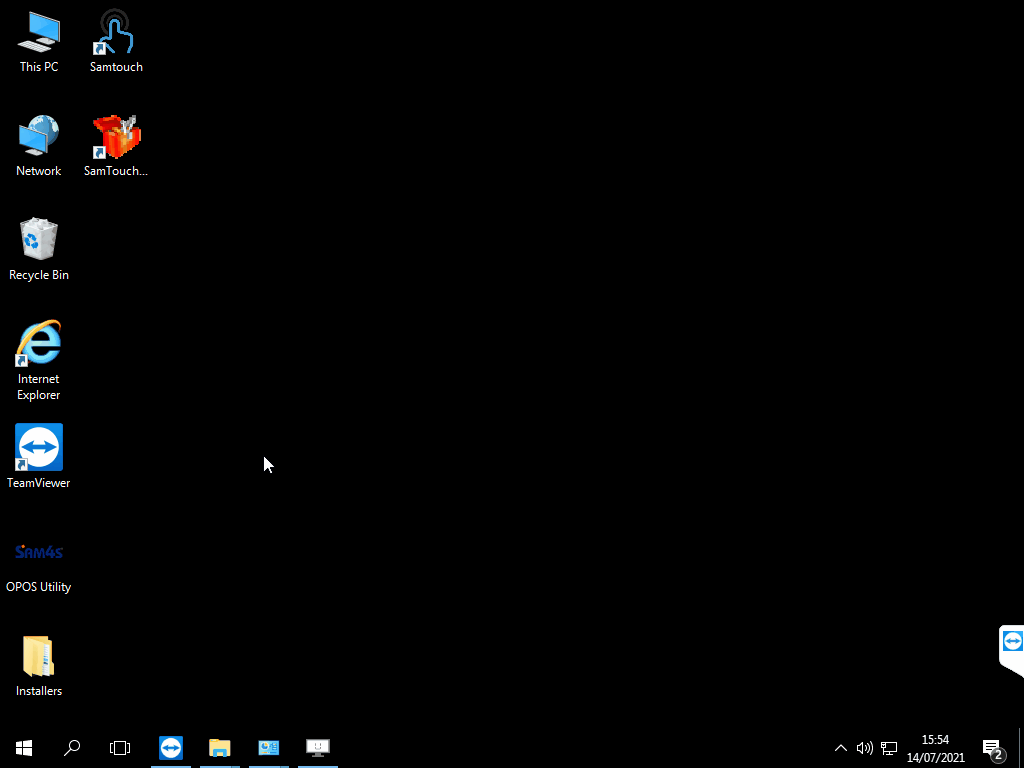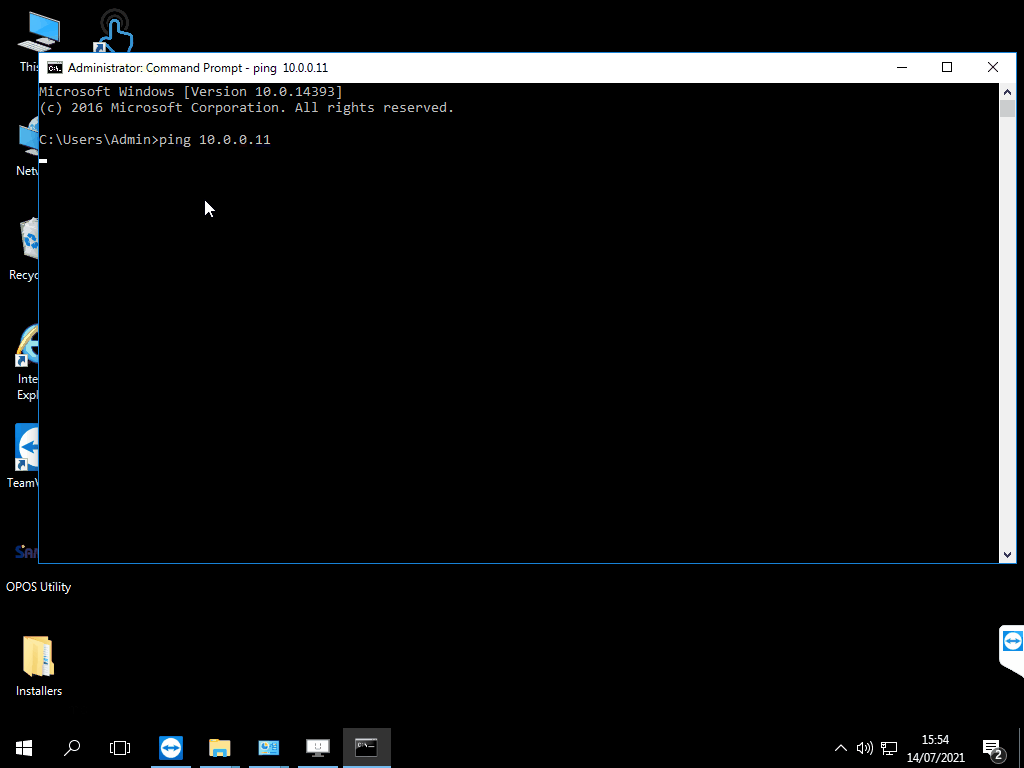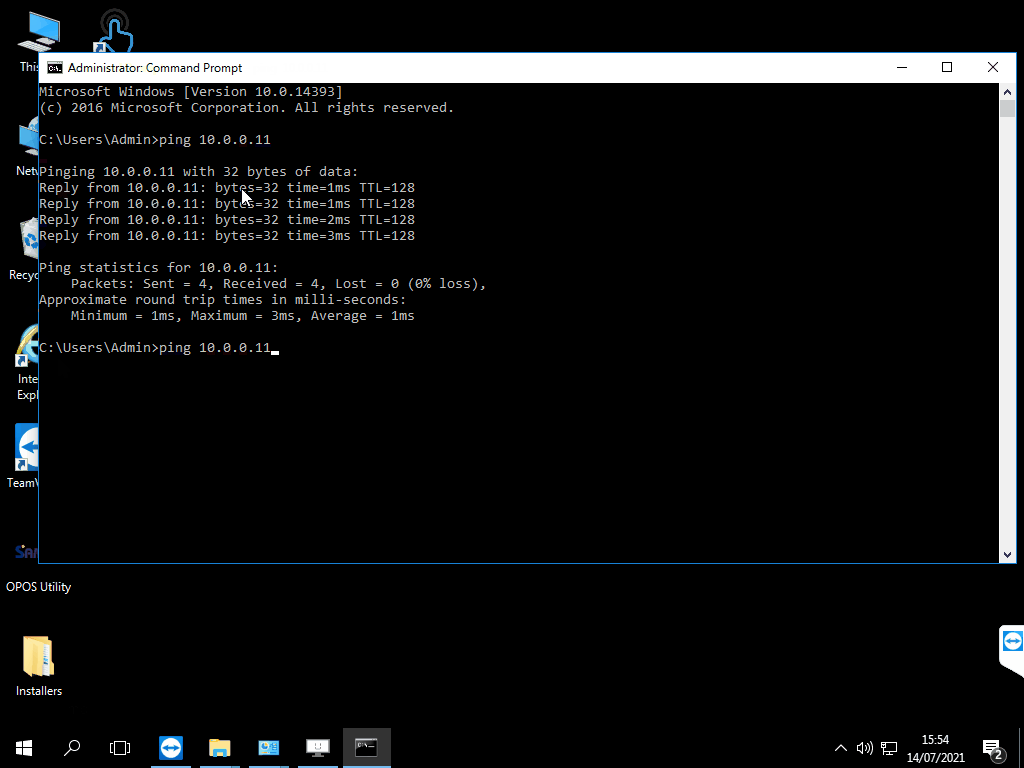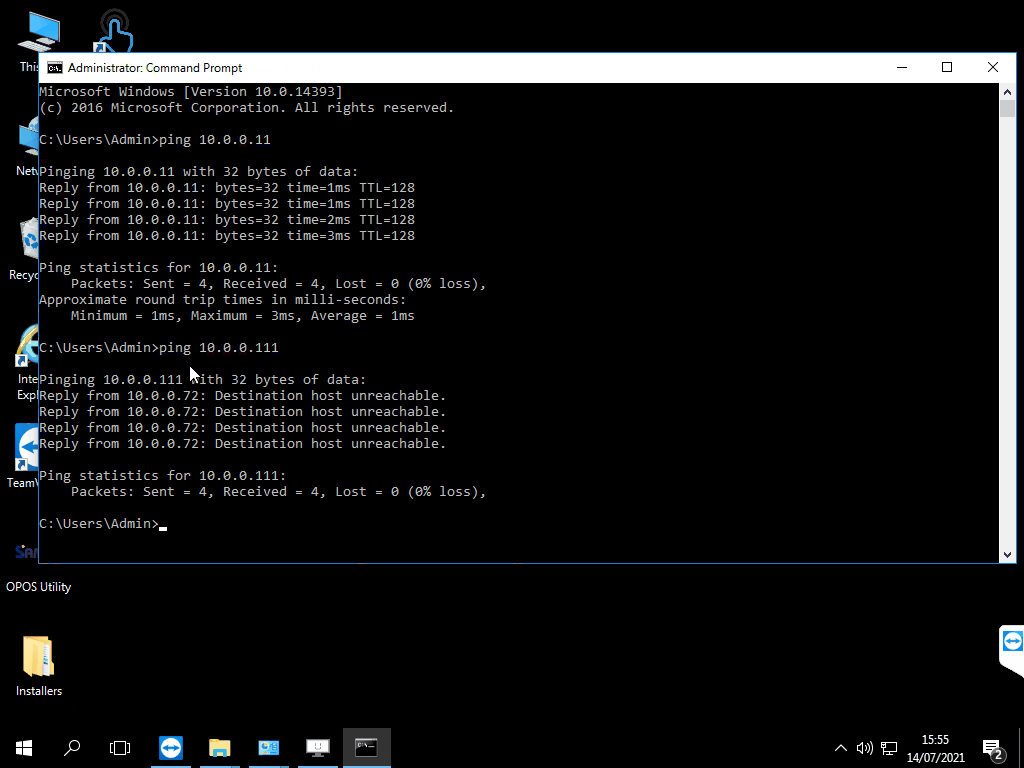
However, if you get Reply from 192.168.1.11: Destination host unreachable this means that it cannot see the other terminal so there is another underlying problem here. This could be any of the following:
- The IP has not been configured correctly, so this will need to be checked on each terminal to ensure the IP address, Subnet and Default Gateway is correct.
- There is a physical issue somewhere, this could be the terminal itself, cabling, the hub and/or the broadband router.
My terminals can ping each other, what now?
If after running a ping command you get a reply from the other terminals, it is highly likely it is something on the terminal itself that is preventing SamTouch from communicating. The first thing to check is to make sure that the terminals are in the same Subnet ID within the SamTouch configuration. If they are, ensure that IPv4 is also set. If after this they are still not working, it is likely to be the Windows Firewall which is preventing/ blocking the terminals from communicating.
Thankfully, the SamTouch folder comes with a a Network Configuration Tool which will add the firewall rules for you to allow SamTouch to communicate. To add these rules, you will need to do the following:
- Navigate to: This PC -> C:\ Drive -> SamTouch
- In here you should have an application called Network Configuration, double click this
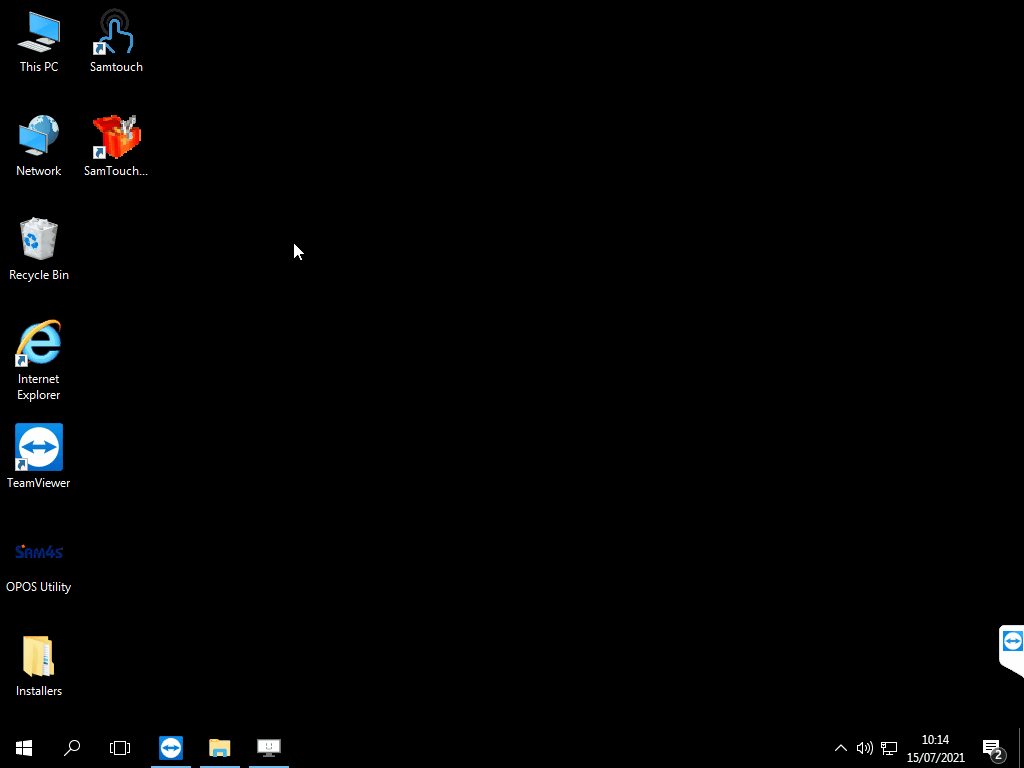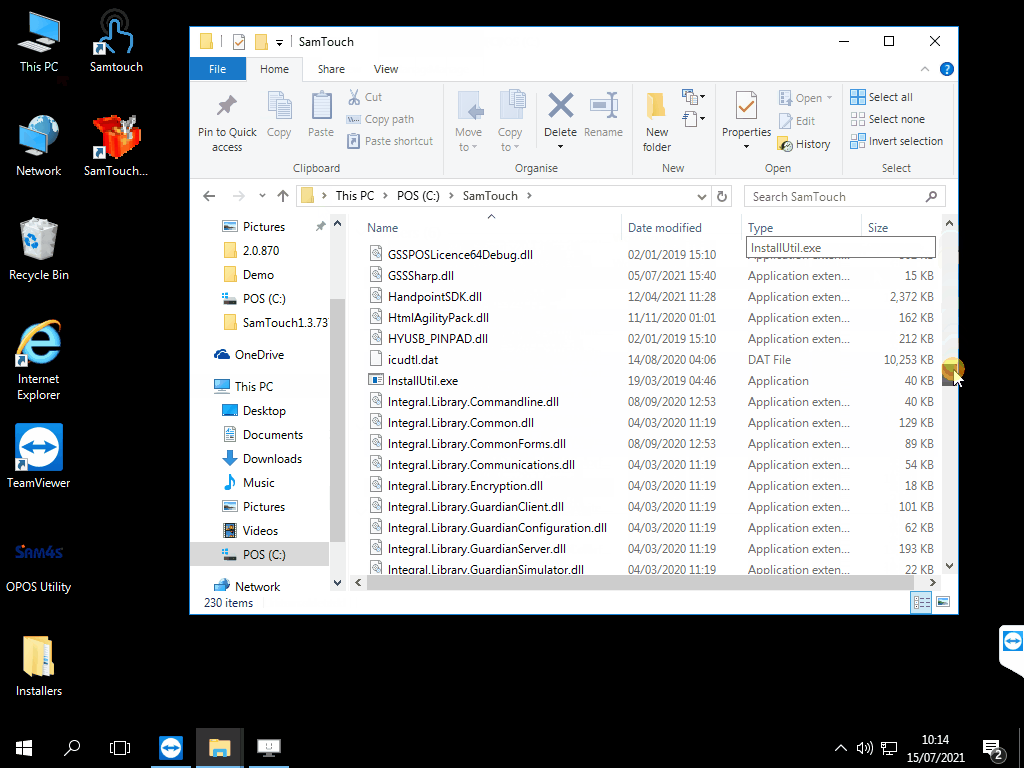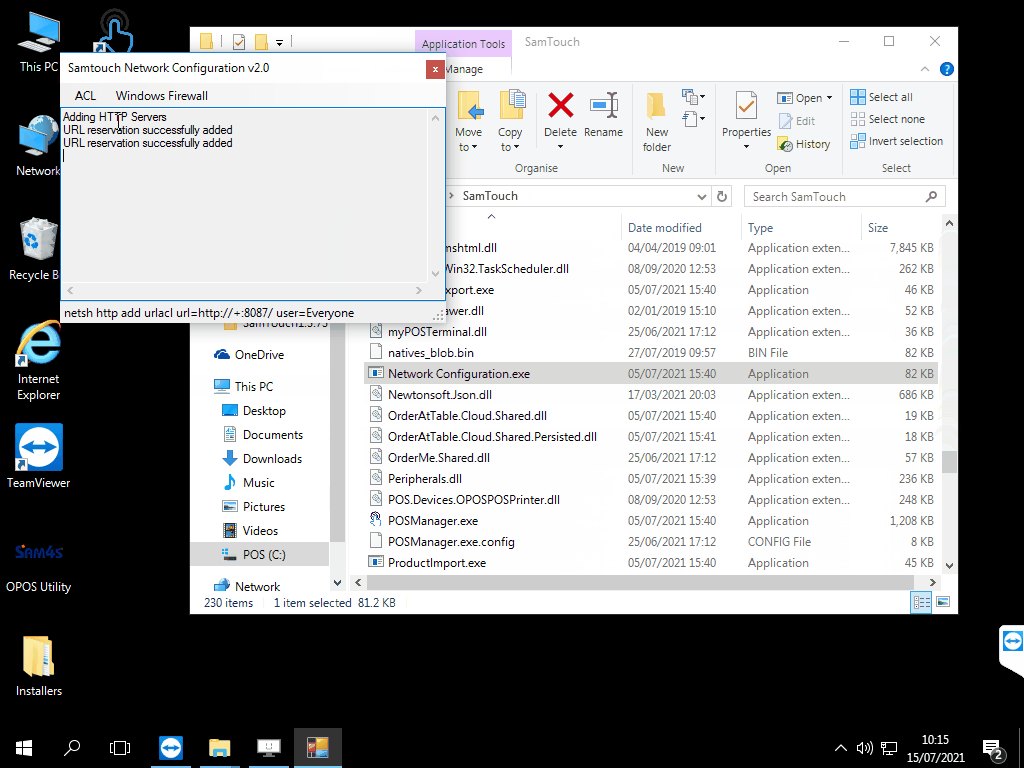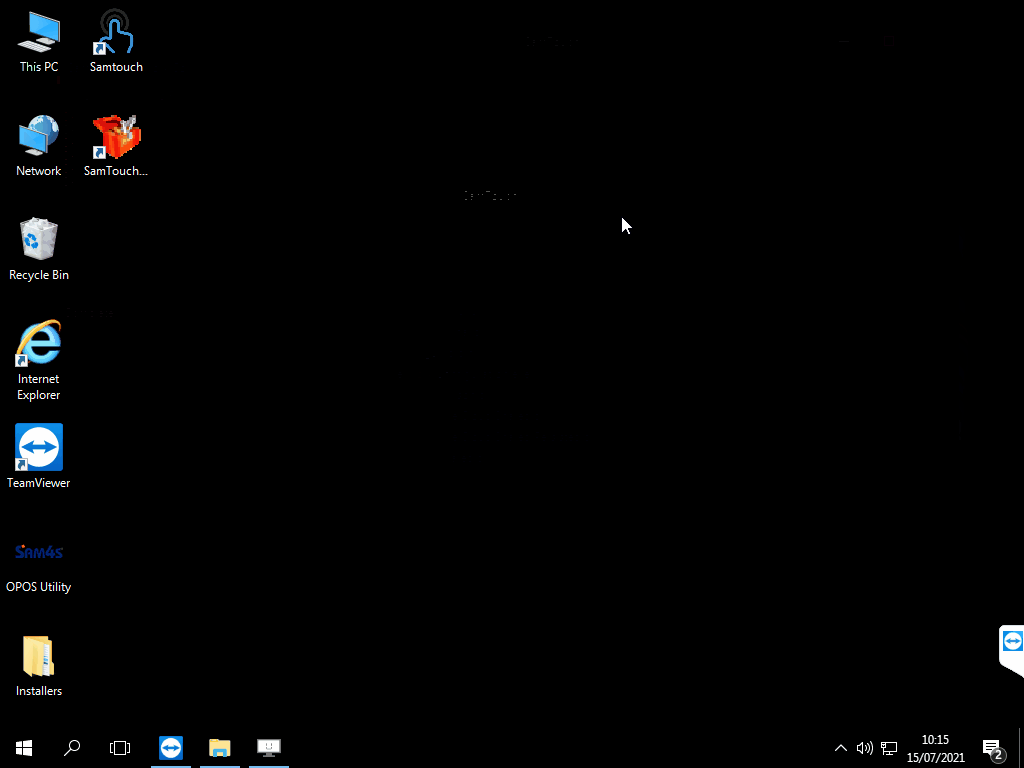
- Click ACL and then Add All. This will add the ACL rules
- Once these have finished adding, click Windows Firewall and click Add Rules. This will add the Windows firewall rules.
SamTouch will now have the correct firewall rules to allow for incoming and outgoing connections. One thing that is worth checking is going to Windows Firewall and checking that there are no blocked connections for anything related to SamTouch, as this would also prevent SamTouch from communicating.
One other thing that is worth checking is whether the terminal’s network is set to Private or Public. If the network is public then this can cause issues with communication, so you will want to change this to private.
In some circumstances it may be the router itself that is blocking the actual connection between the terminals, if after going through the previous troubleshooting options but to no avail, it is very possible that this is where the issue lies.